What is Pneumonia?[]
Pneumonia is a lung inflammation caused by bacterial or viral infection, the air sacs fill with pus and can become solid. The inflammation can affect both lungs which is double pneumonia or just one lung which is single pneumonia.
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs. It’s a more common problem than most people think. Pneumonia is usually a mild disease, but some forms are very dangerous and require hospital attention. Pneumonia can affect a whole lung, both lungs, or even one lobe of the right or left lung. Many different germs affect the lungs and eventually cause pneumonia. Infected lungs shed dead cells and leak fluids which clogs up the air sacs and makes it hard to get oxygen into the blood. http://www.webmd.com/lung/understanding-pneumonia-basics
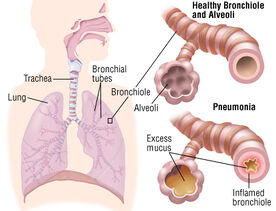
The difference between a healthy bronchiole and pneumonia.
How does Pneumonia Affect the Respiratory System?[]
Pneumonia is a type of acute respiratory infection that affects the lungs. Lungs are made of small sacs that are called alveoli, they usually fill with a air when a person breathes. If someone has pneumonia, then the alveoli are filled with pus and fluid and makes breathing harder and not as much oxygen is taken in.
Most of the time, your airways and nose filter the germs out of the air that you breathe. This helps prevent your lungs from getting infected. Germs can sometimes find a way into your lungs and most likely cause infections. This occurs when: your immune system is weak, a germ is very strong and is present is large amounts, or when your body fails to filter the germs out of the air that you breathe. When you have pneumonia, oxygen may have trouble reaching your blood, therefore if there is not enough oxygen in your blood then your cells won’t work properly. Because of this, pneumonia can cause death. http://www.lung.org/lung-health-and-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/pneumonia/learn-about-pneumonia.html
Signs and Symptoms[]
Symptoms for pneumonia include:
- Cough, producing mucus
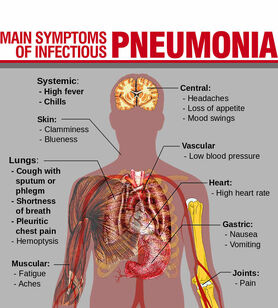
The main symptoms of Pneumonia.
- Fever, which may be less common in older adults
- Shaking, “teeth chattering” chills
- Fast breathing, and the feeling of a short breath
- Chest pain, which is made worse by coughing of breathing in
- Fast heartbeat
- Tiredness, Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Symptoms of Nonbacterial pneumonia include: cough, fever, shortness of breath, and a little bit of mucus when you cough http://www.webmd.com/lung/walking-pneumonia
Diagnosis[]
Pneumonia is usually diagnosed through many different varieties of diagnostic tests. These include chest X ray, blood tests, sputum tests, a chest CT scan, pleural fluid culture, pulse oximetry, and a bronchoscopy. A chest X ray is the best test for diagnosing pneumonia because its painless and it creates pictures and structures of the inside of your chest. http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pnu/diagnosis
Treatment[]
Many doctors usually treat pneumonia using antibiotics. Your antibiotics will usually be chosen based on your age, symptoms, and how severe your pneumonia is. The amount of antibiotics that you take depend on your overall health, and what type of antibiotic you were prescribed. Many victims of pneumonia tend to see results in their symptoms within two to three days of first taking the medication. http://www.webmd.com/lung/tc/pneumonia-treatment-overview\ Specific treatments depend on the type and severity of your pneumonia, your age and your overall health. The options include:
- Antibiotics These medicines are used to treat bacterial pneumonia. It may take time to identify the type of bacteria causing your pneumonia and to choose the best antibiotic to treat it. If your symptoms don't improve, your doctor may recommend a different antibiotic.
- Fever reducers. These include drugs such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and acetaminophen (Tylenol, others).
- Cough medicine. This medicine may be used to calm your cough so that you can rest, because coughing helps loosen and move fluid from your lungs, it's a good idea not to eliminate your cough completely.