What is a Stroke?[]
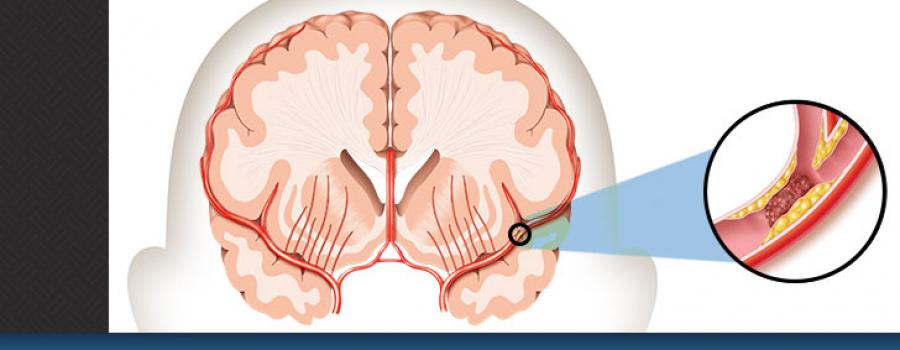
A stroke is a "brain attack". It can happen to anyone at any given moment in time. It occurs when the flow of oxygen-rich blood is blocked out of the brain (ischemic stroke) or another type of stroke could be the rupture of blood vessels in the brain (hemorrhagic stroke). When this happens, brain cells are deprived of oxygen and begin to die, or they rupture and die. When brain cells die during a stroke, abilities controlled by that area of the brain such as memory and muscle control are lost. There are three main kinds of stroke; ischemic, hemorrhagic and TIA. Each having their own causes and effects to the human brain and body. Not mentioned earlier, TIA stroke or transient ischemic attack is also known as a "mini stroke". The most common cause of a TIA is a blood clot or plaque that prevents blood from flowing to your brain.
How does a Stroke Affect the Circulatory System?[]
Strokes occur due to problems with the blood supply to the brain; either the blood supply is blocked or a blood vessel within the brain ruptures. A stroke is a medical emergency, and treatment must be sought as quickly as possible.
Signs and Symptoms[]
In order to spot a stroke there in an acronym that you must follow. It is F.A.S.T. You must proceed with these four steps to be able to know if that person is having a stroke.
F is for face drooping. Does one side of the face droop or is it numb? Ask the person to smile. Is the person's smile uneven?
A is for arm weakness. Is one arm weak or numb? Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
S is for speech difficulty. Is speech slurred? Is the person unable to speak or hard to understand? Ask the person to repeat a simple sentence, like "The sky is blue." Is the sentence repeated correctly?
T is for time to call 9-1-1. If someone shows any of these symptoms, even if the symptoms go away, call 9-1-1 and get the person to the hospital immediately. Check the time so you'll know when the first symptoms appeared.

Diagnosis[]
To determine the most appropriate treatment for your stroke, your emergency team needs to evaluate the type of stroke you're facing and the areas of your brain affected by the stroke. They also need to rule out other possible causes of your symptoms, such as a brain tumor or a drug reaction. Your doctor may use several tests to determine your risk of stroke, including:
Treatment ([1])[]
There are 3 main emergency treatments for a stroke:
- TPA
- Surgery
- Non-Surgical Procedures
TPA (Tissue Plasminogen Activator)
TPA are thrombolytic drugs which are often call clot busters. This can only be given to patients who are having a stroke caused by a blood clot; it can stop a stroke by breaking up that blood clot. This drug must be given as soon as possible and within 4 ½ hours after stroke symptoms begin.
Surgery
In some cases surgery is the best treatment to repair damage after stroke. This could be used to repair dead blood vessels or clean up blood that has pooled in to the brain after hemorrhagic. This could also be useful to prevent stroke from happening again.
Non-Surgical Procedures
Multiple cases of treatment can be performed through a thin, flexible tube called a catheter into the blood vessels or the brain. Many of these procedures are new and experimental and hospitals may be able to go through with them. This type of procedure is being developed to remove build up from arteries and to treat aneurysms.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mm9gpbSZ4Us
What is a stroke?
A stroke is known to occur when the arteries to your brain become narrowed or blocked. Which causes severely reduced blood flow to the brain. Multiple different clots may form which are caused by fatty deposits that build up in arteries which causes the blood flow to reduce severely. Strokes may also cause sudden weakness, loss of sensation, or difficulty with speaking, seeing, or walking. Since different parts of the brain control different areas and functions, it is usually the area immediately surrounding the stroke that is affected.
How do strokes affect the circulatory system?
A stroke may cause a Deep vein thrombosis which is a condition in which the blood clots form in the veins, most commonly the leg veins. These clots can then dislodge and travel through bloodstream to an artery somewhere in your lungs, where they stop the flow of blood. This condition is called pulmonary embolism.
Signs that you are having a stroke:
You can find out if someone is having a stroke by just asking them a few simple questions such as: 1. Ask them to smile if there face looks droopy on one side and fine on the other you must take precautions 2. Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward? Or is one arm unable to raise up? 3. Ask the person to repeat a simple phrase. Is there speech slurred or strange? 4. Finally if you observe any of these signs call an ambulance strokes are very deadly and the longer they last the more damage they will cause.
How is a stroke diagnosed?
Usually people who may be experiencing a stroke it will undergo an MRI. This test can detect changes in the brain tissue and damage to brain cells which would be caused from a stroke. An MRI may be used instead of, a CAT scan to diagnose a stroke.
How are strokes treated?
In some cases, surgery may be required to repair damage after a stroke has occurred to prevent a stroke from occurring. Surgery may be performed to remove blood that has pooled in the brain after a hemorrhagic stroke, or to repair broken blood vessels. Some people may benefit from treatments that are performed through a thin, flexible tube called a catheter into the blood vessels or the brain. Many of these procedures are new and experimental and not all hospitals may be able to do them.
80 percent of all strokes are preventable. It starts with managing key risk factors, including high blood pressure, cigarette smoking, atrial fibrillation and physical inactivity. More than half of all strokes are caused by uncontrolled hypertension or high blood pressure, making it the most important risk factor to control .